Pipe penetrations are one of the most common types of roof penetration in commercial metal roofs. Regarded for their proven record of longevity and value in providing weathertight solutions, a metal roof’s performance can be compromised by improper pipe or flue penetrations to accommodate other building systems. Done poorly, metal roof penetrations can cause leaks, building damage, and unnecessary expenses. When expertly designed and installed, however, pipe and flue penetrations may be successfully integrated into metal roofing systems without compromising performance. Here are five proven and practical guidelines to help avoid problems.
Metal Roof Flue & Pipe Penetration Tips
1. Use Qualified Installers
A qualified roofing installer is the best person to cut and install appropriately flashed and booted pipe penetration. If that isn’t possible or practical, then any penetration installed by another contractor should be fully coordinated with the architect/owner’s representative and the roofing contractor. This is the only way to be sure that the integrity of the roofing system is maintained.
2. Use Only Commercial Materials for Pipe Penetration
Use Only Commercial Materials for Pipe Penetration – To properly seal around the pipe penetration, use only a rubber roof jack made specifically for use with metal roofs. Do not use residential-type roof jacks or those designed for other roof types – they will not last over time. Further, do not use materials that are dissimilar to the standing seam metal roof, such as copper, lead, or galvanized metal roof jacks, which can corrode the metal roof system, or are of inferior quality with a short service life (less than 20 years). Proper commercial roofing products combine an EPDM rubber boot (or silicone for high-heat applications) with a bonded aluminum band to allow a compression seal to be formed at the roof panel.
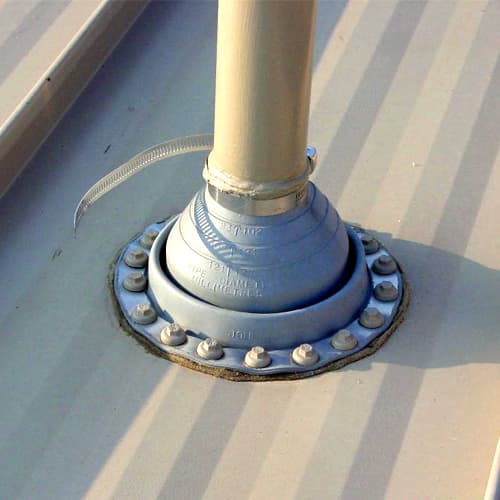

- Standard EPDM roof jacks can withstand temperatures up to 212º and are suitable for most applications.
- High-heat, silicone-based roof jacks can withstand temperatures up to 437º and are suitable for flues.
- Retrofit roof jacks are available in both temperature ranges for applications in which the roof jack cannot be slipped over the top of the pipe.
- Use only tape and caulk sealants approved by the roof manufacturer.
- Use only long-life fasteners at all exposed fastener applications. Note that zinc-plated fasteners will not last for 20 years and will typically void roof warranties for finish and weather tightness.
3. Metal Roof Flue & Pipe Penetration Locations
All planned commercial pipe and flue penetrations should be assessed first to be sure they are not inadvertently creating a potential leak or other problem. Rather, they should be located so they can be properly sealed with no immediate obstructions that would make the seal to the roof unnecessarily difficult or compromise the long-term performance of your pipe or flue penetration.
- Never allow a pipe to penetrate through a standing seam. It is almost impossible to seal around the roof jack and the panel seam in a manner that will be leak free for the life of the roof. Therefore, always locate the roof penetration onto a smooth or flat area of the roof surface.
- Place the penetration in a location that has the least amount of water draining into the immediate area around it.
- Similarly, never allow a pipe to block the water flow down a roof panel and create a buildup of water. When a pipe is encountered that is too large to fit in the flat of the panel without blocking the water flow, use an aluminum pipe curb to allow the water to flow around the pipe and to provide a large, flat area in which to seal the roof jack to the roof surface.
- In Northern areas, vent pipes should be located as high as possible or otherwise protected against sliding ice and snow from above. On roofs with slopes as low as 2:12, sliding snow, impacting an unprotected pipe, can tear the metal roof or shear the pipe off flush with the roof.
4. Allow for Thermal Movement
The metal roof flue and pipe penetration must allow for thermal movement of the roof. Pipes or other penetrations that are rigidly attached to the structure below may not be able to move as the roof expands and contracts. In these cases, the hole in the standing seam roof should be large enough to allow for this movement without the roof panels impinging on the penetration.
5. Check Warranties
If the penetrations are to be included in a manufacturer’s weather tightness warranty, the manufacturer must approve in writing beforehand the materials and methods to be used to install the penetrations. Failure to follow this guideline may result in the penetrations being excluded from the weather-tightness warranty. If everyone involved with the roofing penetrations is aware of and follows these five guidelines, then in the end everyone should be quite happy with the long-term performance of the roof. If not, the potential for roof leaks and other related problems only increases.