Tag: roofing accessories
Why Upgrade a Roof to Metal Panels?
Metal Panel Roof Restoration & Installation
Everything in Order: MBCI’s Online Ordering Assembly Feature
There’s no getting around it. Erecting any building involves thousands of parts. Different sizes, colors, lengths, types – you name it. Depending on the nature of the project, there could be numerous parts to be ordered and accounted for. Although MBCI simplifies the process, it can still be a lot to manage. Until now, everyone has come up with their own method – like the many long-timers who write it all out by hand. But for those newer to the process, it can be overwhelming. Now we’re taking the guesswork out of it and making the process considerably easier, with exciting new user-friendly features on our online ordering platform.
With the new addition of “Assemblies”, you can simply choose which area of a building you’re working on, fill in some details such as panel type, trim condition, attachment type, size, and color, and the system will do the rest of the work for you – making sure you have any necessary fasteners, accessories or other parts, adding everything to your order. No longer will you have to study construction drawings, note fastener types and add everything to your order by hand. No longer will you find yourself on-site without the needed materials. And, even if you do, the online ordering platform is available right from your phone to get whatever you need on the way ASAP.
As Director of Development Tyler Roose says, “We’ve heard testimonials from many, many customers and it’s the only way they like to order anymore. It’s a huge time saver.”
Ready to get started? Head to shop.mbci.com. If you are registered and an existing customer, you should have everything you need to log in. For new customers, simply fill in the requested information and provide your customer number to create an account. If you don’t have a customer number, reach out to your district sales manager or customer service rep.
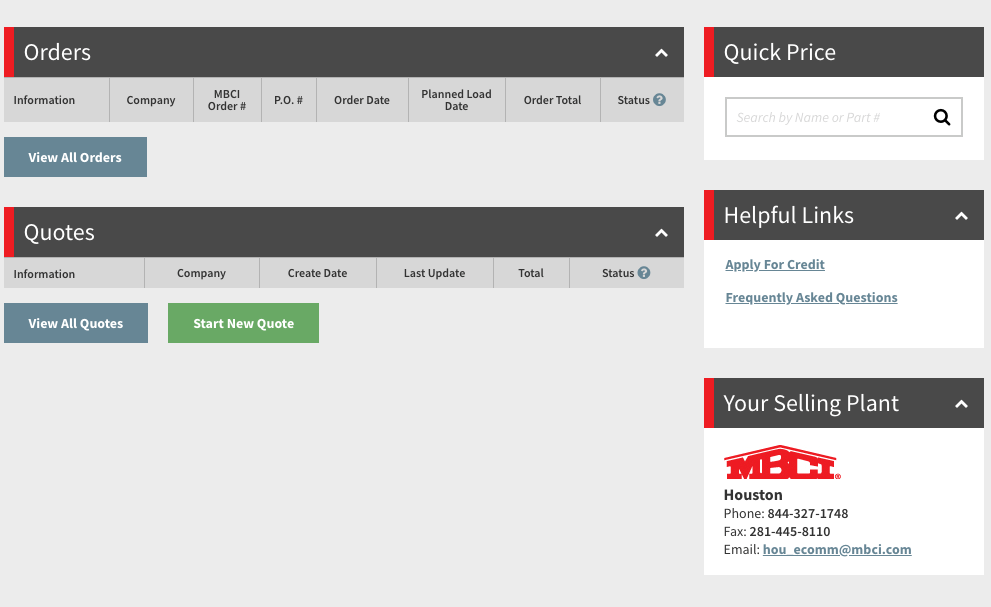
Once you’re logged in, you’ll see the dashboard, which has links to any existing orders, quotes or other information you may need.
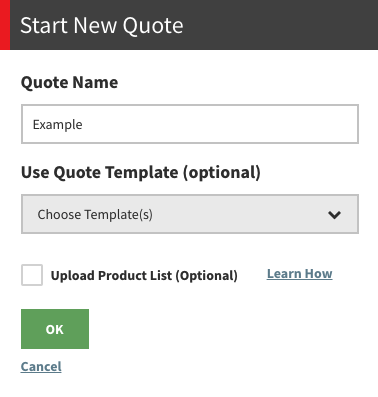
To get started on a new quote, simply click the “Start New Quote” button, which will give you an option to name your new quote and use a template if desired (more on that later).
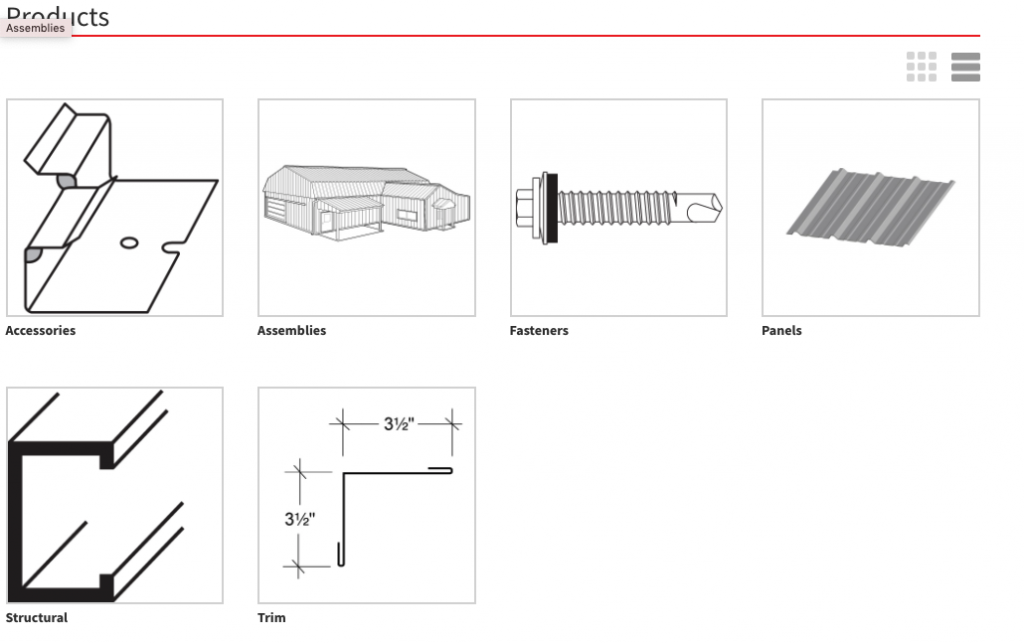
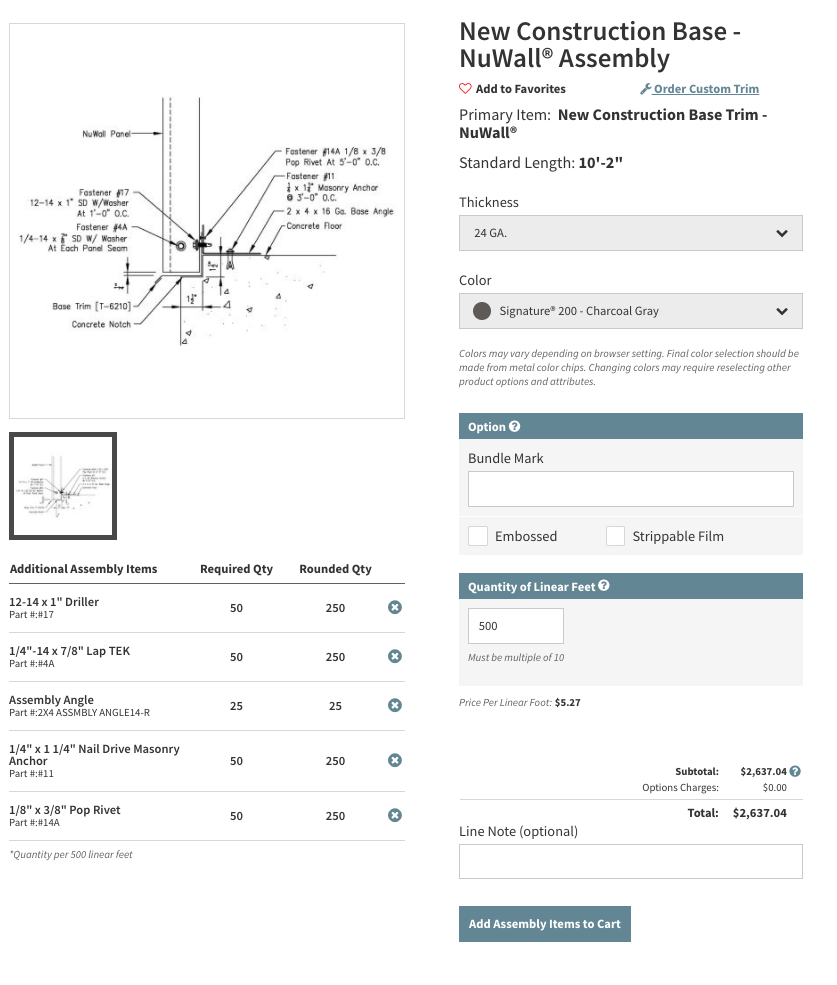
Once you’ve begun a new quote, you will land on the Products page, where you have the option to shop by category, such as accessories, fasteners, panels, structural and trim. However, for this purpose, let’s focus on the newest option: Assemblies.
Choosing “Assemblies” will open a list of component types to choose from. For this example, we’re selecting PBR, but you’ll choose whichever is appropriate to your project. From the next list, select the area you’re working on, such as eaves, gutters, valleys, corners, bases, etc.
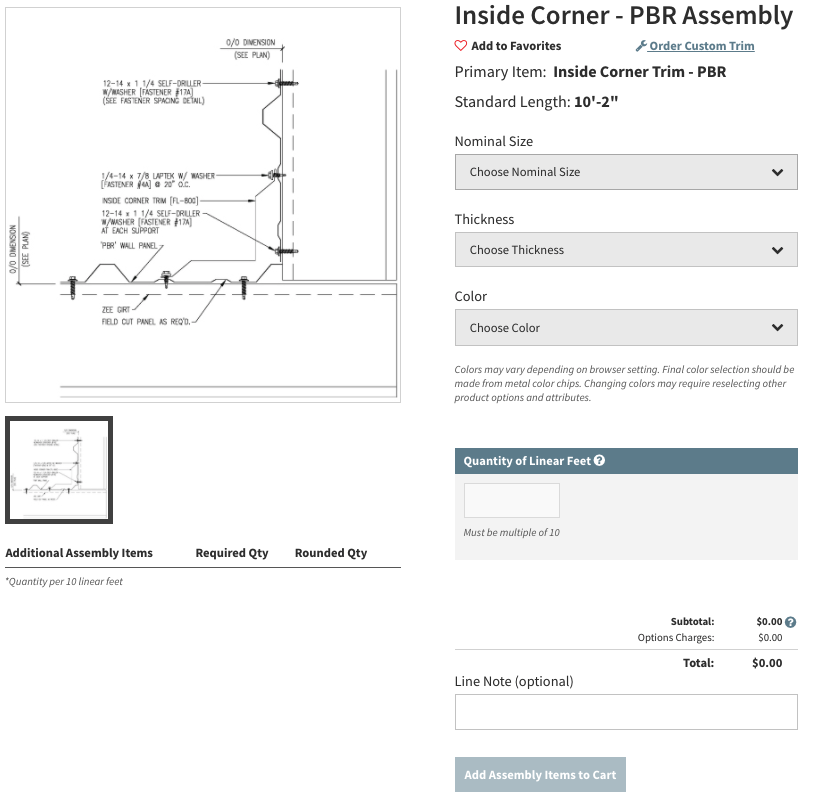
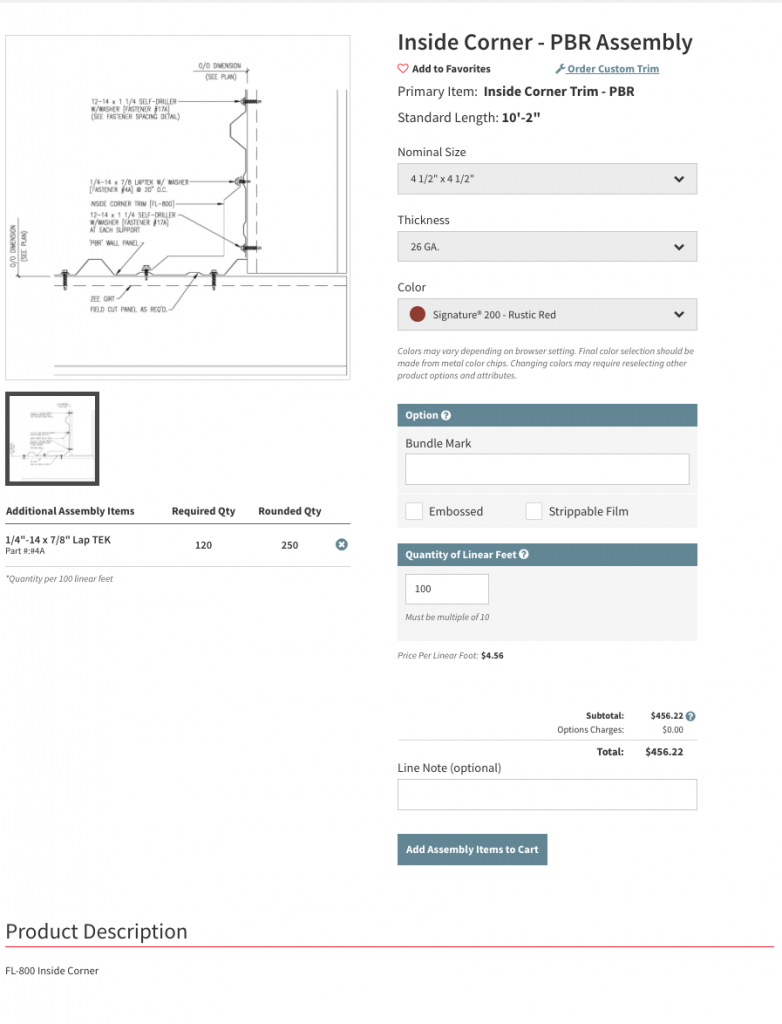
Once you’ve selected your assembly, the form will prompt you to choose details such as thickness, color, lineal footage of the assembly being used, and further options depending on the assembly and area you’re working on. Then, all the core trim items as well as necessary fasteners, sealants and accessories are automatically added to your material list for review. Notice the additional parts automatically added on the PBR form. If satisfied with your work, click “add to cart”, and a more formal review can now be completed once all parts from the project are accounted for.
Now you can simply repeat this process for whatever other areas you need. You can save and share this quote with others who may need to review and approve. If you anticipate needing similar orders in the future, choose the “Save as Quote Template” option in the dropdown box. The next time you have a similar project, choose this option when you start a new quote, then simply make whatever changes are necessary – colors, lengths, quantities, etc. – and you’ll be done with your order in much less time than with previous methods.
If for any reason you need to make changes to a quote, simply use the “Modify Quote” button at the bottom of the quote page.
Be sure to check out the other handy features on the online ordering site, such as related literature, documents and parts at the bottom of each product page and in catalogs. You can also search by keyword or use the navigation at the top for anything you might be looking for.
We hope you’ll take the time to learn the new system. It’s sure to save you innumerable hours in the long run. And if you get stuck or run into any problems, we’re here to help. Refer to the FAQ and don’t hesitate to get one of our sales individuals involved. We are all fully versed on online ordering and happy to help.
Tips for Selecting and Field Applying Touch-Up Paint
Metal roofing and wall panels routinely come from the factory pre-finished a durable, baked-on paint finish that covers the Galvalume®-coated steel surface. This production occurs in a controlled environment, which helps create a consistent product, and allows metal panels to last decades with minimal maintenance. It turns out, however, that the biggest threat to a metal panel’s paint coating can happen during panel installation. Tools, fasteners and other installation-related items and activities can scratch or damage the finish, requiring touch-ups to the paint. If you experience this, here are some touch-up paint tips to keep in mind.
Assess the Damage
First, determine how noticeable the scratch is. Do you have to be close to see it, or can you see it easily from several feet away? Generally, if the scratch isn’t noticeable and has not penetrated the Galvalume coating, its best to refrain from doing a paint touch-up. This is because touch-up paint can’t match the fade resistance of the original baked-on pre-finish, and if the Galvalume is still intact, it will still protect the steel beneath the scratch.
On dark or bright colors in particular, the touch-up paint will fade much more quickly than the original paint. Often, the end result is that touch-up paint is more noticeable than if the scratch is left alone. On the other hand, if the scratch is noticeable and needs a touch-up, there are some best practices to follow. It’s important to note though, that if a large area of the panel is damaged (more than 10–15%), then it’s best to just replace the panel.
Getting the right touch-up paint
Metal panel manufacturers recognize that there may be a need for minor paint touch-ups in the field. So, most offer small containers of paint conducive to field work. These paints are specifically formulated to match standard color offerings, and have properties that make them compatible with the factory finish. Therefore, it’s important to always buy touch-up paint from the manufacturer that produced the original panels. Never ask a paint store to match colors based on a piece of panel or trim. Doing so may get a color match, but it won’t contain the other protective properties of the paint coating you receive from a manufacturer.
Choice of touch-up paint application
Touch-up paint for field application is often available in three types of containers: paint pens, small bottles and spray cans. Usually, the best choice for a scratch is a paint pen. Touch-up paint pens have small, precise tips that can fit into scratches, allowing it to only apply paint where needed. For larger scratches or scuffs, manufacturers offer bottles of paint (with a small brush) similar to those used for nail polish. Generally, these are best for dings on the panel.
Spray cans are also available, and are ideal for painting small accessories like plumbing vent pipes. Don’t use spray cans to conceal a scratch because they apply much more paint than necessary. This can cause unsatisfactory results as the paint weathers and fades differently than the original paint.
Using touch-up paint
When performing a paint touch-up, it’s important to make sure the area in and around the scratch is clean and dry. Wipe down the area as needed, then dry it completely before applying any paint. Afterward, paint the surface using the least amount of paint necessary. This eliminates excess paint on the pre-finished panel. Paint pens are ideal for this since they apply less paint than a nail polish-type bottle or spray can. Once the touch-up paint is on the panel, it will need time to dry. During drying, make sure that dust or other contaminants do not embed into the wet paint.
Consult the metal panel manufacturer
To ensure you or your maintenance professional properly select and apply touch-up paint, be sure to check all warranty and installation requirements and resources with the metal panel manufacturer. They can help ensure you get touch-up paint that matches the paint originally used on your panels and that you take the right steps to ensure warranties remain intact. MBCI offers metal panel touch-up paint for industries and applications including:
- Agricultural
- Architectural
- Commercial and Industrial
- Insulated Metal Panels
- Residential
- Standing-Seam Metal Roofing
For more on metal roof and wall panel finishes, colors and touch-up paint techniques, contact your local MBCI representative.
Cutting Metal Panels Properly On Site
Cutting metal panels on site is an often-necessary part of installing metal roofing and wall panels. However, using the right tools and methods to ensure the panels remain damage-free is vital. Using the wrong tools can result in rust, rust stains, the voiding of warranties and diminished building service life. In this blog post, we’ll share several common field-cutting techniques and best practices that help ensure good results.
Maintaining Longevity When Cutting Metal Panels On Site
When metal panels are made in a manufacturing facility, the tools and methods used to cut the coated metal coil help protect the cut edge from deterioration like corrosion. When cutting metal panels on a jobsite or in the field, protecting any cut edges is just as important. To understand how to field-cut metal panels without sacrificing the quality and protection delivered from the manufacturing facility, you must first understand the what protects the panels. Most often, metal roof and wall panels are fabricated from Galvalume®-coated steel coil because of its proven longevity. Not only does the Galvalume coating protect the surface area of the metal panels, it has also been shown to be effective along the thin edges of the metal too, as long as those edges are cut properly.
During fabrication, the Galvalume metal panels are cut to length either by shearing while flat before entering the roll former, or by means of a profile shear as the panels exit the roll former. Either method tends to “wipe” the Galvalume coating across the cut edge of the metal panels. This provides superior cut-edge protection from corrosion.
Likewise, when panels arrive on site, any needed field cutting should address the same concerns of protecting the edge of the steel from corrosion. Of course, there are ways of doing the field cutting correctly. However, there are also poor strategies that can lead to real problems. The following are examples of common field cutting tools and the best practices for good results.
Common Tools and Methods for Cutting Metal Panels On Site:
Aviation Snips
Red and green aviation snips are a good choice for small cuts on metal panels, such as around pipe penetrations. These snips will wipe the Galvalume® coating in the same way as factory shears, making them a good choice.
Electric Shears
Electric shears are optimal when making lengthier cuts along the steel, such as cutting a wall panel at a corner or at a door opening. These shears take a ¼” strip of metal out of the panel during the cutting process, which tends to leave both sides of the panel smooth and flat along the cut. Like the aviation snips and factory shears, electric shears will wipe the Galvalume coating and protect the edges.
Mechanical Shears
Mechanical shears are an add-on tool that fit onto a battery-operated impact or screw gun. These shears do not take any metal out of the panel and will leave a slightly wavy edge. Mechanical shears are an excellent choice for bevel cutting standing-seam panels at hips and valleys, since they too wipe the Galvalume coating over the cut edges to offer protection.
Nibblers
A nibbler is a great tool for cutting across corrugations in wall panels to create openings for windows, doors and similar structural additions. A good nibbler typically costs $500-$700 (currently), but is well worth it if you often cut corrugated metal panels. The punch and die in the nibbler tends to wipe the Galvalume across the cut edge as it punches out small, half-moon shaped pieces of panel. However, because these little metal pieces will fall away from the cut, it’s important to contain them so no one walks on them. Otherwise, they can embed in the soles of installer’s shoes and create scratches in roof panels when they walk on the roof.
Skill Saw
Skill saws are an ideal tool for cutting metal panels because of their versatility. This tool can cut either across or parallel to corrugations, whether straight or at an angle. When using a skill saw, it is critical to use a saw blade that cuts cool. Otherwise, the Galvalume coating can melt along the cut edge and become ineffective. In particular, do not use an abrasive blade, which will generate heat and damage the coating.

Additionally, its vital to avoid cutting panels on the roof or above other panels. A skill saw blade will throw considerable amounts of steel debris into the air and down onto any panels below. This debris, called swarf, will quickly rust and ultimately cause rust spots in the panels. If enough swarf gathers in one spot, it can rust through the panel.
Steel swarf, like this collected at the ridge will rust through the panel.
Which Tools Should To Avoid When Cutting Metal Panels On Site:
Tools that should never be used include:
- Torches
- Cut-off saws
- Reciprocating saws
- Hacksaws
- Grinders
All of these tools will melt the Galvalume® coating, causing edge rust just like an abrasive blade would. These tools also throw a lot of steel debris (swarf) onto the panels they cut. This debris will be hot and will embed into the panel coating. This can cause rust spots and bigger problems down the road.
In conclusion, using the right tools and following metal panel manufacturer recommendations when cutting metal on site will help ensure that the panels remain damage-free and the final installation will be a fairly seamless process. Using the wrong tools can result in rust, rust stains, and the voiding of warranties. For more on best practices and recommendations for on-site cutting and installation of metal panels contact your local MBCI representative.
Metal Roof Seaming: Best Practices for Ensuring Weathertight Seams
It would seem logical that the most important field installation process for a standing-seam metal roof is the actual process of creating the weathertight seams that connect the metal panels together and ensures the structural integrity of the roof. Perhaps for many different reasons, however, this critical seaming process is not always given the proper attention it deserves, nor are installers given the proper training required to ensure installation runs smoothly. This approach can cause some serious issues, not the least of which is the voiding of a manufacturers warranty or the discovery of roof leaks and the resulting damage.
To help, here are some best practices for readily and successfully carrying out the metal roofing seaming process:
Personnel
Because of the critical nature of seaming metal roofs, the crew members doing this work should be properly trained. Team members who will be performing this work should not perform the seaming without having participated in the appropriate installation training required to ensure the seaming process is appropriately managed. Most roofing manufacturers offer installation training that many installers take advantage of—and this training opportunity should be taken advantage of by the staff who will be doing the seaming.
Seaming Equipment
It is very important that the seaming equipment being used is matched to the specific roof panel system being installed. Manufacturers routinely rent out this equipment in order to be sure that the metal panel profiles are installed properly and are not compromised through the use of generic equipment or that of another manufacturer. Using the wrong equipment can end up being costly for everyone if panels and seams are ruined in the process.
Hand Crimper
As metal panels are set in place, they are often secured with metal clips, spaced according to engineering and construction needs. Hand crimpers are used to form the seams around the clips as well as any end laps. This process must not be overlooked as improper hand tooling is the number one cause of faulty seaming. To ensure costly mistakes aren’t made, follow the process described in the “Field Seaming Tool Manual”. This manual should be provided with the equipment and reviewed in training.
Electrical Sources
The next step will involve the use of an electric seamer which obviously needs a source of electricity to operate. However, not just any electrical power source will do. Almost all professional seamers have an AC/DC motor that will require 10 or 15 amps and 120 volts. A dedicated electrical circuit—preferably from a temporary electrical pole or an existing building electrical panel—is the best and most reliable way to go. A generator with 15 amp capacity dedicated to be used only for the seamer (in order to avoid power surging) may be acceptable as well. In either case, the power line to the seamer needs to be 10-gauge (minimum) cord. It should also be no more than 200 feet long (to avoid power drop).
Electrical power sources that are NOT acceptable include outlets from a powered man lift or a generator that is not dedicated to only the seamer. (This includes a generator that is part of a welding machine.) Check the manufacturer’s requirements for any other restrictions that can damage the seamer. Skipping this step can place the responsibility for repair or replacement onto the installer.
Electric Seamer
Once all panels are in place, the hand crimping is done and the power source is set. Then, electric seaming takes care of finishing the roofing system. Again, consult the seamer manual for proper procedures, including which direction the seaming should be done. (Seaming can either be done up or down the roof depending on direction of roof installation.) The electric seamer includes a switch for the operator to control the starting and stopping of the process.
On low-slope roofs, the operator should walk alongside the seamer to be sure nothing is in its path and that the seam is done properly. While stopping and re-starting is fine, the seamer should never be removed in the middle of a seam. Doing this makes it very difficult to set it back in exactly the same spot again. If something appears to be wrong with the seamer or the seams being produced, then don’t keep using it. There is no point in damaging multiple roof panels if any one panel indicates that things aren’t going right. In this case, contact the manufacturer right away for assistance or replacement of the seamer.
Safety
Electrical seamers are heavy and—if not used and secured properly—can cause harm or injury. Therefore, they should always be tied off with a safety line—the same type used for workers—not a common rope and definitely not the electrical cord. The safety line should be properly secured to the seamer and then attached to something rigid on the building. Never attach this to a person who could be pulled off of a roof by it.
Cleaning
Before use each day, check the electric seamer and remove any oils, debris or dirt. Make sure the seamer is unplugged from the electrical power source before you begin cleaning. Also, check the grease level in the machine daily and only add a little bit (2-3 pumps from a grease gun) as needed. Too much will cause the grease to leak out onto the roofing.
Following these pointers should help assure the safe and efficient use of the right seaming equipment when installing roofing panels. To find out more about proper seaming or to schedule training, contact your local MBCI representative.
Appropriate Standing Seam Clips for Roof Panels
Part of the beauty and appeal of standing seam metal roofs is that the fasteners holding the metal panels in place are concealed. That gives the roof its clean, continuous appearance that is often desirable, but it also avoids the issue of potential roof leaks around exposed through-fasteners. Concealed fastening doesn’t mean that there aren’t any fasteners, though, it just means they are installed out of sight – underneath the panels. The industry standard approach is to use a metal clip that fits over the edge of a panel and that is secured with a screw type fastener to the structure or substrate below. Then it is covered by an adjacent panel or trim. The important thing to know is that not all panel clips are made the same – for good reasons.
What determines the type of panel clip to use? Here are the most common things to keep in mind:
The Manufacturer
Each manufacturer of metal roofing typically has a range of metal panel types, profiles, and brands that have their own traits and characteristics. As such, they need clips to match and fit with the manufactured panels. Hence, the first place to start with panel clip selection, is for the roofing manufacturer to be clear on the options and choices available that are compatible with their roofing products.
Building Size and Type
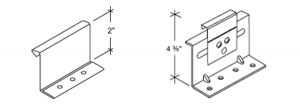
Manufactured metal buildings that include metal roofing commonly use very predictable, coordinated systems. Accordingly, a standard, one piece, “utility clip” is commonly used, primarily for snap together roof panels, on metal buildings that do not exceed certain widths causing undue expansion and contraction. One piece clips allow the roofing panels to expand and contract within the clip profile, but there are limits based on the amount of movement tolerated. Alternatively, in projects where the roofing is attached to something other than a metal building frame or where standing seams are used to secure the panels together, it is advisable to use a two-piece or “floating” clip. In these cases, a base piece is secured to the structure or substrate and the clip fits both into the base and over the roofing panel where it is seamed or folded into the vertical leg of the panel. Using this approach, the clip expands and contracts directly with the metal panel thus moving across the base and keeping the roofing attached.
Insulation
Roof insulation comes in different thicknesses, appropriately so for different climate zones and different roof designs. Since energy codes require at least some of the insulation to fit between the underside of the metal roofing panel and the structure (i.e. above the metal roofing purlins), the metal panel clip needs to be the right height to reach the full height of the insulation up to the top of the roof panel. Hence, manufacturers offer different sizes and heights of panel clips designed to work with different heights of insulation. In many cases, they also recommend the use of a thermal spacer underneath the clip to separate it thermally from the steel structure below. Note that the thermal spacer thickness is dependent on the insulation thickness over the steel purlin only, not the thickness of any insulation under the purlin.

Other Factors
The panel clips connect the roof panels to the roof structure, so they need to be installed in a manner that allows them to do that job under normal and demanding circumstances. The driving issue in this case is not keeping the panel down, but preventing it from blowing off in a strong wind. Therefore, a structural engineer or other design professional may need to determine the proper spacing of the clips, the type and size of fasteners (i.e. screws) to use, or similar important details. Similarly, the proper installation of clips so that they seat and nest the way they are intended, means that qualified and certified installers / erectors should be used. In this way, roofing crews with the needed experience and training can help assure that the whole roofing system, including the panel clips, are installed properly.
To find out more about the most appropriate panel clips to use on a metal roof that you are involved with, contact your local MBCI representative.
Built to Move: Building for Expansion and Contraction with Standing Seam Roofs
Standing seam roof (SSR) systems are built to move, designed to account for necessary—and often substantial—expansion and contraction due to thermal conditions. In fact, for many builders, this fact is one of the main reasons SSRs are such an attractive option.
Even with this expectation baked into the mix, many contractors and installers may still make a wrong turn when tying the SSR into adjacent structures and other building edge conditions. By not allowing for that same expansion and contraction on trims and transitions, problems can ensue.
Fixed and Floating Clips
One main consideration in planning for this movement is the clip type used. Standing seam metal panel clips are designed specifically to interact with their corresponding roof panels in order to allow movement (both interior and exterior) caused by thermal changes. The clips, which are part of the concealed fastening system used with SSRs, provide improved aesthetics in addition to durability and protection from the elements.
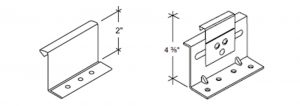
The two main options are fixed clips (one-piece) and floating/sliding clips (two-piece). Fixed clips are limited by and dependent on the substrate’s ability to expand and contract with the roof system, whereas floating/sliding clips permit the panels to expand and contract within the clip itself. These clips will allow for greater thermal movement of the panel, which is independent of the substrate while still ensuring the panel remains secured. Regardless of which clip is utilized, you are not going to stop the expansion and contraction. You can, however, have some control of the direction of movement, and, therefore, can address or compensate for the degree of this movement when tied into adjacent structures.

Standing seam roofs with floating/sliding clips require one end of the panel run to be “pinned” and the other end to be “moveable” in order to permit expansion and contraction. The “pinned” point of the system is typically the low eave, although it doesn’t have to be. There will be instances when it becomes beneficial to “pin” the roof at the complicated transition or tie-in point and design the roof system to expand/contract outward from this location. This can eliminate potentially “troublesome” areas from the equation on having to deal with the roof movement, and in turn can make them easier to install and have greater weathertightness success.
With all this in mind, it is important to always check with the manufacturer to determine the best clip and design layout to use with any given SSR system and be aware of how much and in what direction the expansion and contraction is going to occur.
Tying In
Not only does the building move, but anything it ties into has to be able to permit that movement, e.g., the edges or perimeter of the buildings. Manufacturers can provide both longitudinal and transverse transitions that allow for thermal movement so that when they tie into an adjacent structure it doesn’t restrict the panel from moving. Not adequately compensating for or preventing that movement entirely can lead to potential pitfalls, such as oil canning. It could also lead to fasteners backing out and slotting of holes. Bottom line, any time that we try to confine or restrict the roof from doing what it was meant to do (move!), we inevitably run the risk of damaging the panel not just aesthetically but more importantly, from a weathertightness standpoint.
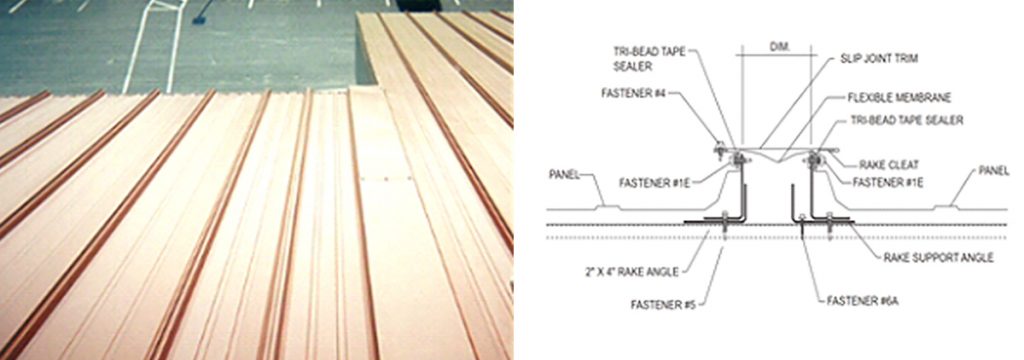
The Role of Expansion
Issues can arise not just when tying panels into adjacent structures. Because of the roof’s size and magnitude of potential movement, you may/will have to implement expansion/contraction capability of various degrees into the perimeter of the roofing system itself. In these cases, this is why manufacturers offer roof accessories as ridge expansions, edge trim expansions, panel expansions, gutter expansions and other details to account for not only the roof movement but the perimeter trims that are secured from the roof system to the wall system.
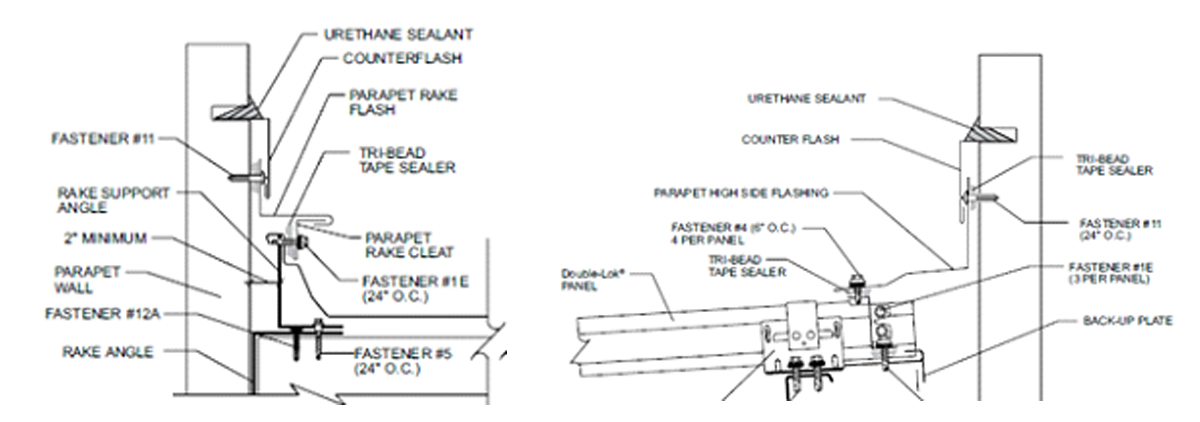
Know Your Details
The key takeaway here is to remember that if you’re considering a standing seam roof for a project, then you need to make sure that the designer looks at every detail from the manufacturer and accounts for movement of the roof panel, such as how it ties into adjacent structures or simply how the edge or perimeter of the building is terminating to make sure they permit that expansion and contraction. Know what you’re buying and understand that if the roof you’re purchasing is meant to expand and contract, everything that ties into it has to be able to expand and contract as well.
To find out more about how to correctly install your standing seam roof, contact your local MBCI representative.
Preventing Roof Damage from Rusted Fasteners
These days, the majority of metal roofs are made from Galvalume coated steel, which typically carry a warranty against perforation due to rusting for a period of 20 years. A study on Galvalume standing seam roofs (SSR) conducted at the behest of the Metal Construction Association (MCA) showed that a properly installed Galvalume SSR can be expected to last 60 years or more. However, the caveat is “properly installed”. One of the major issues that will drastically reduce the service life of a Galvalume-coated roof is the use of non-long-life fasteners in exposed locations.
Anytime you have an exposed fastener on a metal roof, you risk rust—the term commonly used for the corrosion and oxidation of iron and its alloys. While a little rust might not seem like a big deal, its presence can actually be a harbinger of severe damage to your metal roof panels if not caught early, or ideally, stopped before it ever has a chance to start.
The issue is most prevalent on R-panel roofs due to the use of exposed fasteners. And even with standing seam roofs, which use clips and are typically referred to as a concealed fastener roofs, there are exposed fasteners as well, most often at the eave, the end laps and at trim, such as ridge flash, rake trim, and high-eave trim.
Prevention
The best recommendation for any exposed fasteners (meaning they are exposed to the weather and other harmful elements), is that they should be long-life fasteners. When you don’t use long-life fasteners, they start rusting with exposure to moisture and, over time, the rust virus stretches down to the roof, causing severe and often irreparable damage.
Suppose you have a metal roof that is 10 to 15 years old. Depending on the environment, the roof could be in excellent shape—except for where those screws are; you can have holes right through the roof at the fastener locations. More people than ever are starting to realize they’re supposed to use a long-life fastener, in a case like this. We see a lot of roofs when we inspect them for weathertightness warranties. What often happens is a worker on the roof may have just grabbed some screws that were handy without thinking about the kind of screw or the inevitable chemistry that could potentially cause rusting. Or, you may have a situation where there is some type of accessory put on the roof by another trade, perhaps a plumber or an HVAC installer—and maybe they didn’t use long-life fasteners.
The best recommendation to mitigate this potential problem is two-fold. First, make sure roofing installers know to use a long-life fastener at every exposed location. Secondly, make sure that every other contractor working on the roof that you’re responsible for knows to use long-life fasteners with whatever they’re doing.

What if rust does occur?
One question frequently asked is: if the fasteners do become rusty, do you have to replace all the panels? If you catch the problem before the rust virus makes its way down to the roof itself, you can just change out the screws. However, if the rust has compromised the roof, you very likely would have to change out all the panels, at the least everything that has been affected—just because of one little spot. Truthfully, if the rust is in one spot, it’s probably all over.
Another thing worth mentioning is if aluminum panels are used along with typical long-life fasteners, it could still rust, especially if the roof is exposed to salt spray (think close to the coast). The answer in this case is to use a stainless steel screw, which are long-life fasteners (but not all long-life fasteners are stainless steel).
Be aware from the start.
It’s crucial for installers and contractors to take notice and order the right fasteners from the start so that problems can be avoided.
Also, after some wear and tear, if subsequent work is done on the roof, everyone involved should take note. For instance, you buy a building and somewhere down the road you decide to frame out a small office and add a bathroom. You’d need a water heater, so a plumber goes on the roof, puts in pipe penetration and doesn’t use long-life fasteners. The onus would be on the owner to ensure that everyone performing work on that roof—no matter when—is using long-life fasteners.
Conclusion
The best-case scenario with a metal roof is to get the right fasteners to begin with. However, if the roof is already installed, the next step is to be on the lookout for rust and if you notice it, consider that it might be because of the fastener.
If that’s the case and you catch it early—when it’s just the screws that are rusting but the rust virus hasn’t yet transferred down onto the roof, you can just change out the screws with the proper long-life fasteners. We recommend doing a roof inspection at least once a year. If you see any loose or rusty screws, replace as needed.
For more information on MBCI’s broad selection of metal roof and wall panels, contact your local MBCI representative.