Tag: installation
How to Retrofit Existing Roofs with New Metal Roofing Systems
In our prior blog post, Benefits of Roofing Retrofits with Metal Roofing Systems, we looked at the benefits associated with retrofitting an existing building with a new metal roofing system. In this discussion, we will look at several ways to do it.
New Sloped Roof Over an Existing Flat Roof
Buildings with flat roofs can be retrofitted with light-gauge steel framing systems to create a new sloped metal roof. Such systems can be installed directly over existing roofing membranes and structures, subject to appropriate structural engineering review. These systems typically use light-gauge (16 gauge to 12 gauge) steel framing installed directly above the existing roof to create a sloped plane. Regardless whether the existing roof structure is steel, wood or concrete, the new, lightweight framing system can be designed to disperse roof loading appropriately and connect securely.
The physical footprint of the existing roof, the type of framing system employed, and any special rooftop conditions will typically control the final geometry of the new sloped roof. A low-slope application (less than 2:12) can be selected based on economy and configured to discharge rainwater off of the roof. High-slope applications (greater than 2:12) are typically selected to improve and update the look of an existing building while improving long-term performance. Once the metal framing system is in place, then standing seam metal roof panels are commonly installed, creating a ventilated attic space in the process.
Retrofit Roofing Panels
Low-slope metal roofing can be a great choice when a fairly utilitarian solution is needed for improving overall roofing performance. Exposed fastener systems can be used to allow direct installation of the new roofing panels over existing metal roofing or some other materials. Roofing panels specifically designed for retrofit applications typically have a rib spacing of 12″ on center with a rib height of just over an inch. The minimum slope for such a panel is 1/2:12. Any existing lap screws must be removed from the existing roof before the new panels are installed. The new retrofit panels are then attached with screws that fasten through the existing panel major ribs and into the existing purlins.
A New Standing Seam Roof
In some cases, an existing sloped roof may have another roofing material in place that is nearing the end of its service life. In that case, a new long-lasting, standing seam metal roofing system can be installed directly over the existing roof. Some systems will require a simple sub-framing system that allows the new roof to be installed directly over the existing. Retrofit roofing systems such as this can be UL-90 rated and FM Global rated. Other strategies exist to increase the energy efficiency of the building when adding new standing seam roofing, such as adding unfaced fiberglass insulated between the existing and the new roof and to vent the cavity between the old and new roofs by adding vent strips at the eaves, plus a vented ridge to allow air intake and exhaust. This method works well with roof slopes of 3:12 or greater.

End Results
Regardless of the specific system selected and designed, installing a retrofit metal roofing system allows the existing roof to remain in place, which saves on labor costs. It also minimizes the chance for water entry into the building during the roofing process and provides for a safer working environment. Existing rooftop equipment, vents, or light-transmitting panels can be accommodated by any of the systems described.
According to the Metal Construction Association (MCA), “retrofit metal roofing represents an economical and functional solution for building owners who want to beautify their existing structure or correct performance issues related to aging roofs and out-of-date materials. They have been employed in millions of square feet of existing commercial, industrial, retail and education facilities. The result is a new code-compliant metal roof that will last for 60-plus years, providing higher energy efficiency by reducing heat gain through the roof in summer months and reducing heat loss during winter months.”
To find out more about these retrofit systems, contact your local MBCI representative.
Can Metal Roofing Be Installed Over Shingles?
Why Upgrade a Roof to Metal Panels?
Metal Panel Roof Restoration & Installation
How to Avoid Common IMP Installation Mistakes
Insulated metal panels (IMPs) are ideal for many roofing and wall applications. They are considered a top-of-the-line choice known for their superior insulation value, high performance air barrier, design flexibility, and fast installation. The simplicity of installation creates a high-performance building envelope. The many design options provide a versatile building solution for commercial, industrial, and institutional projects.
Sounds great, doesn’t it? What’s the catch? Well, those benefits won’t mean much if proper care is not taken during the installation process to ensure you’re getting what you paid for. Potential consequences can span the gamut—from minor aesthetic headaches to extremely costly errors such as leaks and structural issues.
Here are some ways to avoid common pitfalls when installing IMP panels on your next metal wall or roof project.
1. Pay attention to the manufacturer’s product installation manuals.
Installation manuals are not just for show! Even the most experienced installer should read, review and understand the installation guide before installing IMPs, and the panels should always be installed in accordance with the project’s installation drawings.
Don’t simply rely on the “what-you’ve-done-before” mindset. Take the time to review the specifics for every individual project. In addition to providing the information needed to execute a successful install, it can also give installers an opportunity to build upon their own knowledge base. One of the most common errors is related to proper receipt and handling of the panels. Investing a few minutes before the project starts and at the start of each day to review key topics helps avoid costly errors and improves production.
If you have a question or something does not seem right stop and call the manufacturer. It is always best to address a problem up front than try and fix a problem after the building is in operation.
2. Equipment check. Do you have what you need?
To keep your IMP installation on track, it’s imperative to ensure you have the equipment you’ll need for the job. Does your project need one or two forklifts, is a crane a better option? Will your project include longer-length IMPs being installed in a vertical orientation? If so, you may need special lifting equipment so as not to damage the panels. Whatever the details, crews need to be prepared to receive a project’s specific materials on site. A little advance planning will ultimately save you time and money by reducing labor and avoiding costly mistakes.
3. Don’t assume every IMP application is the same.
All buildings are not created equal. Just because a construction crew has had experience installing insulated metal panels on past jobs, doesn’t mean they can assume the process will be exactly the same every time. There will always be specific conditions and variables that need to be taken into consideration. Techniques used for vertical industrial panels will be different for horizontal architectural panels.
The vapor barrier (a key function of an IMP) is a great example of how a miscalculation can be problematic. Depending on the panel, the vapor barrier may be applied either at the factory or at the jobsite. If the project calls for a cold storage environment, the “warm” side of the vapor barrier will be on the exterior. Alternatively, a commercial or industrial application generally calls for the vapor seal to be on the opposite side of the panel. Confuse placement of the seal and you’re bound to run into problems down the road.
4. Be on the lookout for creases, buckles and framing alignment.
A crease or buckle on the face of a panel might seem like no big deal, but that couldn’t be further from the truth. In fact, framing alignment is one of the most critical aspects to ensure a proper fit-up of the construction as a whole. In terms of the panels themselves, not only will a framing misalignment not LOOK right but can also cause numerous efficiency and performance issues. Installing inexpensive shims can avoid panels needing to be replaced.
Additionally, make sure the first panel is plum and square, if you start right it is much easier to finish right.
Purlins must be level and square and all framing and bracing should be installed before installing panels. (The IMP manufacturer should specify the amount of tolerances allowed.) Also, take care with caulking and taping, foam-to-foam connections (in order to mitigate potential vapor leaks), seaming, and lap joints.
Attention to detail will avoid costly mistakes.
5. Always think ahead.
Being proactive may be the most important piece of advice construction crews need to hear.
For one, be sure to have a panel surplus on hand. You may be of the mindset that ordering extra panels is at worst a waste or at best, not worth the effort. This is a common judgement error that often leads to installation delays. If a crew has only ordered the exact number of panels needed for a job and there is any damage to the product, whether prior to delivery, on-site or during the installation, there a risk to the project schedule. Waiting on replacement panels can wreak havoc on schedules, especially with panels that may need special manufacturing due to custom components, finishes or colors. What do you do with extra panels you don’t need on the initial installation? Building owners can hold on to any surplus panels to be used as replacements, as needed, over the lifecycle of the building. A little preparation today can go a long way.
Other best practices include understanding the project’s site conditions and ensuring crews remain crews up to date on proper installation techniques—including staying current with training and certifications.
By taking this advice to heart, you can exponentially increase your ability to enjoy the many benefits of IMPs and be confident in your investment. For more information on MBCI’s insulated metal panels and proper installation guidelines, we encourage you to contact your local MBCI representative or visit our website.
Protecting Metal Panels from Rust
One of the many benefits of metal panels that contributes to their strengths is the fact that there are so many rust-resistant coating options with different levels of protection, making them a great option for virtually any environment or any budget. That said, though, missteps during storage, as well as during and after installation, can leave you with unwanted corrosion, i.e. rust. Factors such as improper storage, improper cutting, or other elements the metal might come in contact with can wreak havoc that are beyond the manufacturer’s control.
Regardless of the finish you have—painted, unpainted, high-end coatings or standard coatings—here are some simple installation and care instructions that can help further maintain the longevity of your metal panel product.
Preventing Rust When Materials Are Delivered
Proper material delivery/site storage is the first step to preventing rust. Be certain to check your panels while uncrating after storage on site for any early signs of corrosion, such as black discoloration or white rust/residue on them. This is a sure sign that that panel has been improperly stored and water has not been able to properly evacuate the panel bundles. Do not install any panel on which this has occurred, as the panel finish has most likely been compromised due to improper storage. If you go ahead and install it, that panel is going to continue to corrode and eventually lead to further rust/corrosion.
Make sure that you’re not trapping any sort of moisture in between the metal panels or restricting them from being able to drain when stored on site. Although the panel itself is corrosion-resistant, if you subject it to repeated and significant water being trapped in between the sheets by either not storing the material out of the mud and ground water, or if you’re not sloping the material bundles in such a manner that they can drain, then the result can yield “wet storage stains.” Therefore, if you want to prevent any sort of damage due to improper site storage, you must make sure that the panel is able to drain while stored and, if possible, tarp to resist heavy moisture concentrations such as snow and ice during inclement weather if necessary.
Preventing Rust During Installation
Next, let’s look at some installation no-no’s that WILL most definitely eventually lead to rust—and things to avoid. The first is the accumulation of drill shavings. Whether it’s a roof panel or a wall panel, when you’re installing the screws, even if you’re pre-drilling for the screws, you’re going to generate metal shavings. If those metal shavings are not removed and left to sit or cling to the sheeting those shavings will rust and will stain the roof or wall sheets. The shavings are uncoated/raw metal with no corrosion protection that can and will rust quickly. Eventually, the shavings may wash off or be blown off the roof or wall, but might not be until after they’ve stained the sheeting, thus leaving you with an issue to remedy and, since the “culprit” is gone, questioning if it’s just a stain or something more serious.
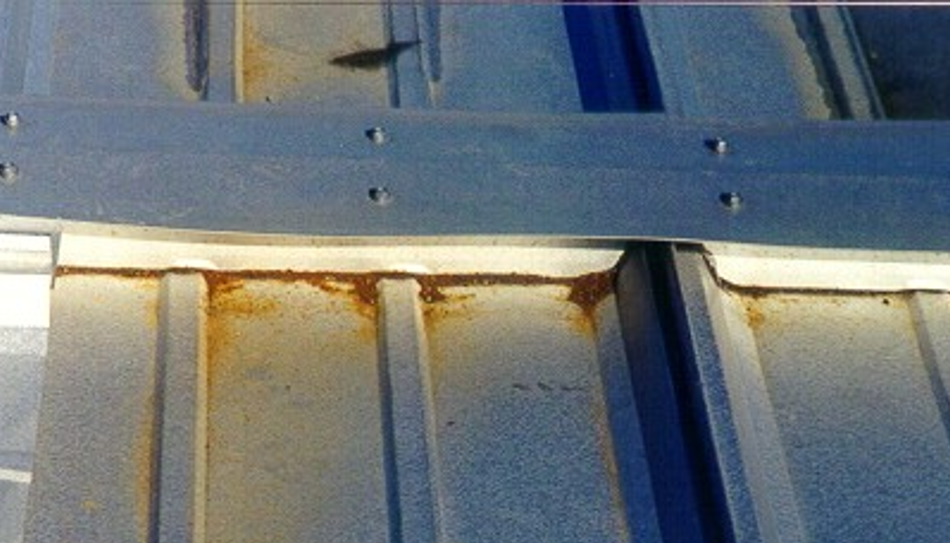

Remove the shavings as soon as you can to mitigate this issue. Additionally, if you’re going to do any field cutting, you need to do so via a shearing process utilizing the proper tools, such as electric nibblers, hand snips or electric shears. Any other type of cutting can cause the edge of the base material to become exposed and no longer protected by the Galvalume and painted coatings as they become disrupted. Using tools such as a “hot” saw, abrasive blades or even a reciprocating saw leads to a tearing motion rather than shearing motion, which will strip the metal of that protective coating; over time it can start to rust.
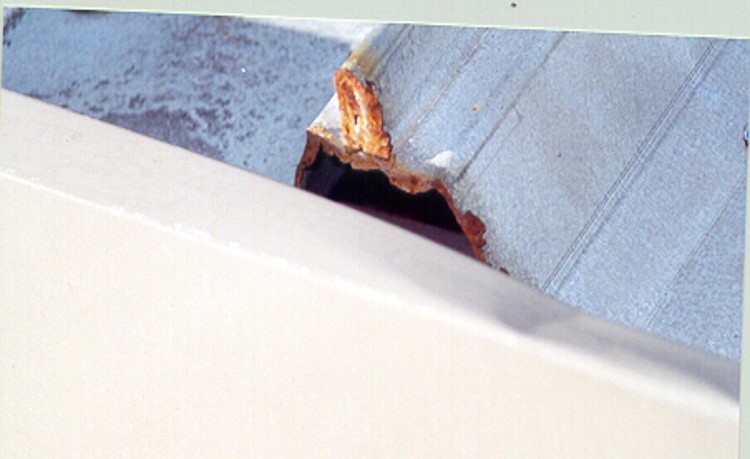

Graphite is another corrosive element that should be avoided as it is not a friend to Galvalume metals. Therefore, stay away from writing on your Galvalume material with pencils because over time the graphite will react, break down that protective layer, and lead to corrosion. If you do write on the panels with a pencil, make sure you clean it off. The best solution is to use permanent markers/Sharpies or dry erase markers.
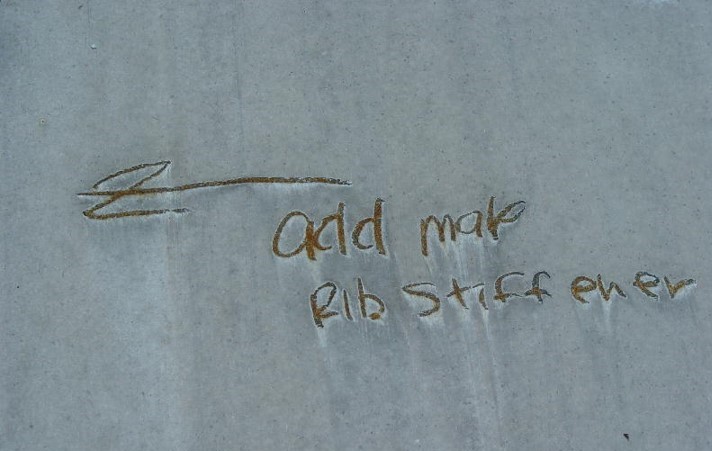
Watch out for overspray from any adjacent wall coatings or finish systems like Stucco or similar masonry products, which can also damage panels if not removed promptly. And be certain not to rest the base of any metal panel in direct contact with material that is corrosive, such as concrete, or in such a manner that water can become trapped behind the panel and not able to drain. Industry recommendation is to maintain an eighth of an inch to a quarter-inch gap at the base of all your wall panels for not only expansion/contraction but for proper drainage and to prevent contact with dissimilar/corrosive materials.
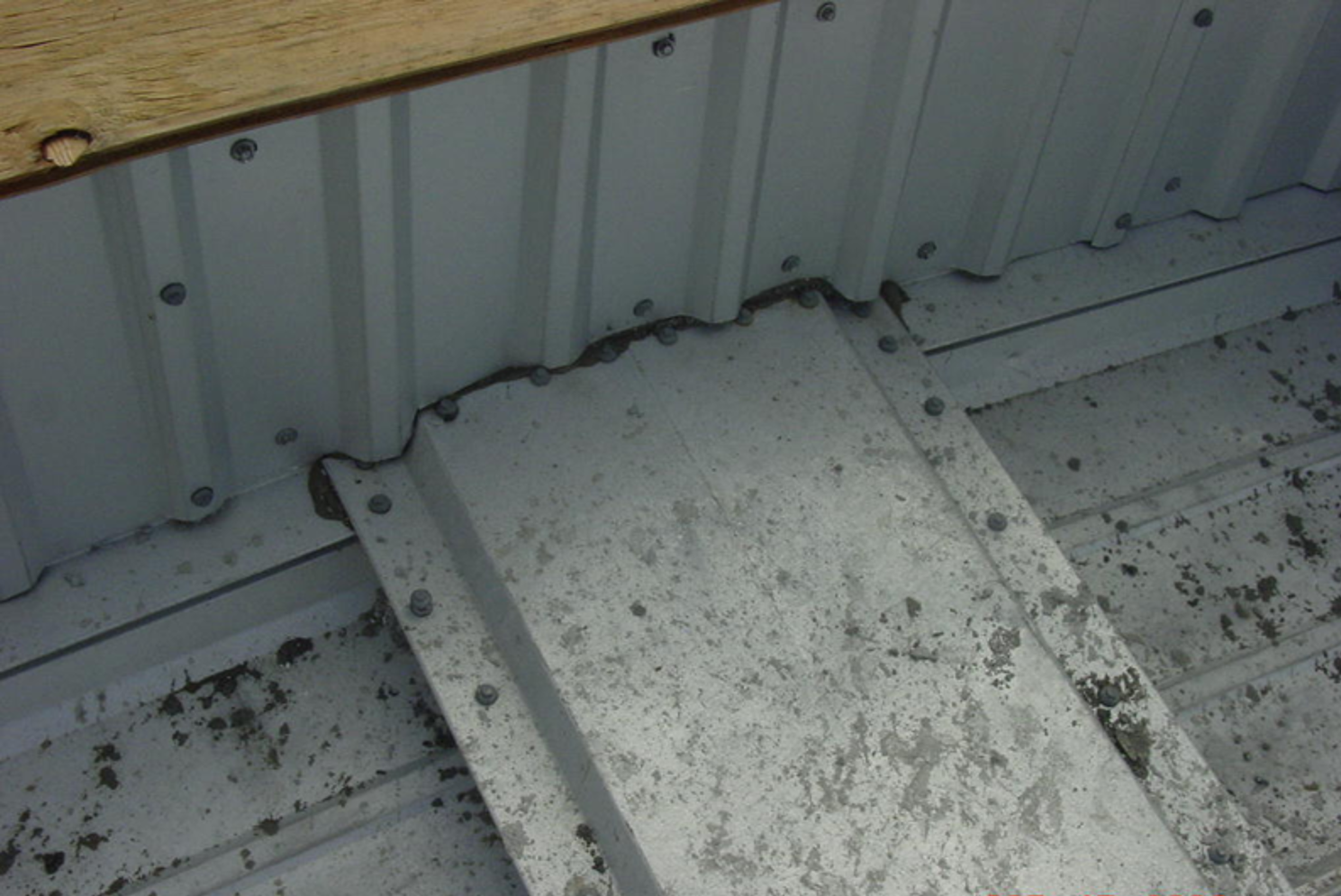

Preventing Rust After Installation
Although Galvalume—whether bare or painted—is highly corrosive-resistant by nature, it too has its Kryptonite. Post-installation, the most important thing is to make sure you’re not adding something to the roof that’s going to react chemically/negatively with the Galvalume finish/coatings. For instance, many people don’t recognize that if they have mechanical units on a roof, the condensation that comes out of those mechanical units, when deposited directly onto a Galvalume panel over time, will lead to corrosion and rust. This condensate should either be filtered before exited onto the roof panel or drained via piping and not directly onto the sheeting.
Contact with dissimilar metals, whether it be via incorrect type or method attachment from metal signage, solar panels and snow retention can be another major factor in post-installation corrosion. Panels must not come in contact with or be exposed to the runoff from the following metals: copper (lightning arrest systems, flashing, roof jacks, HVAC drainage); lead (roof jacks, pipe flashing); iron (pipes or soil); and, as previously noted, metal shavings.
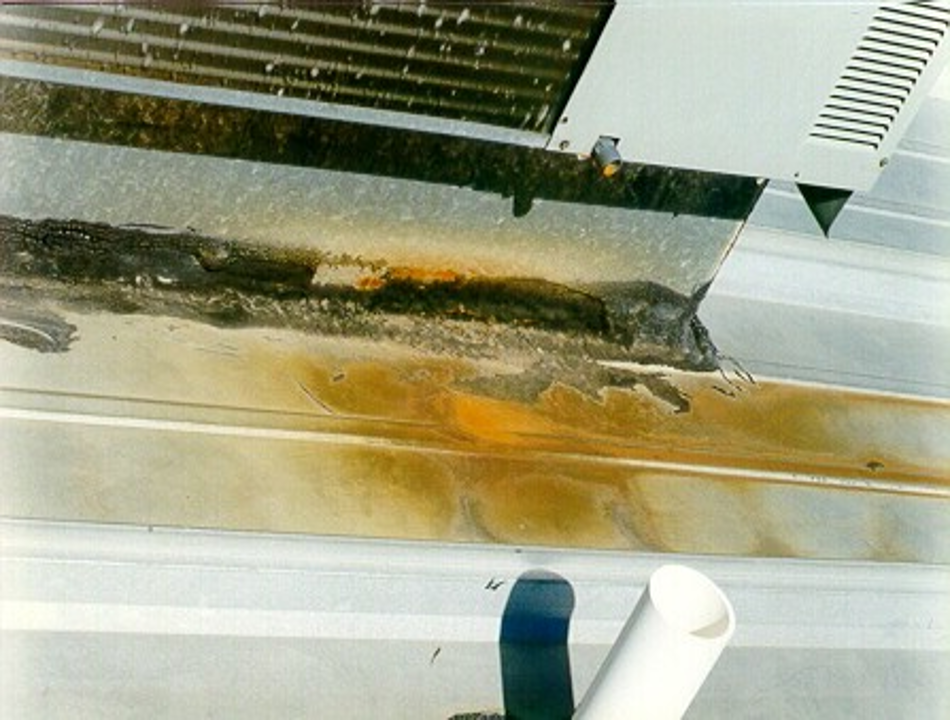

Post-installation, panels must also not come in contact with or be exposed to the runoff from chemicals, such as acid from batteries and acid washing brick, and even pressure-treated lumber.
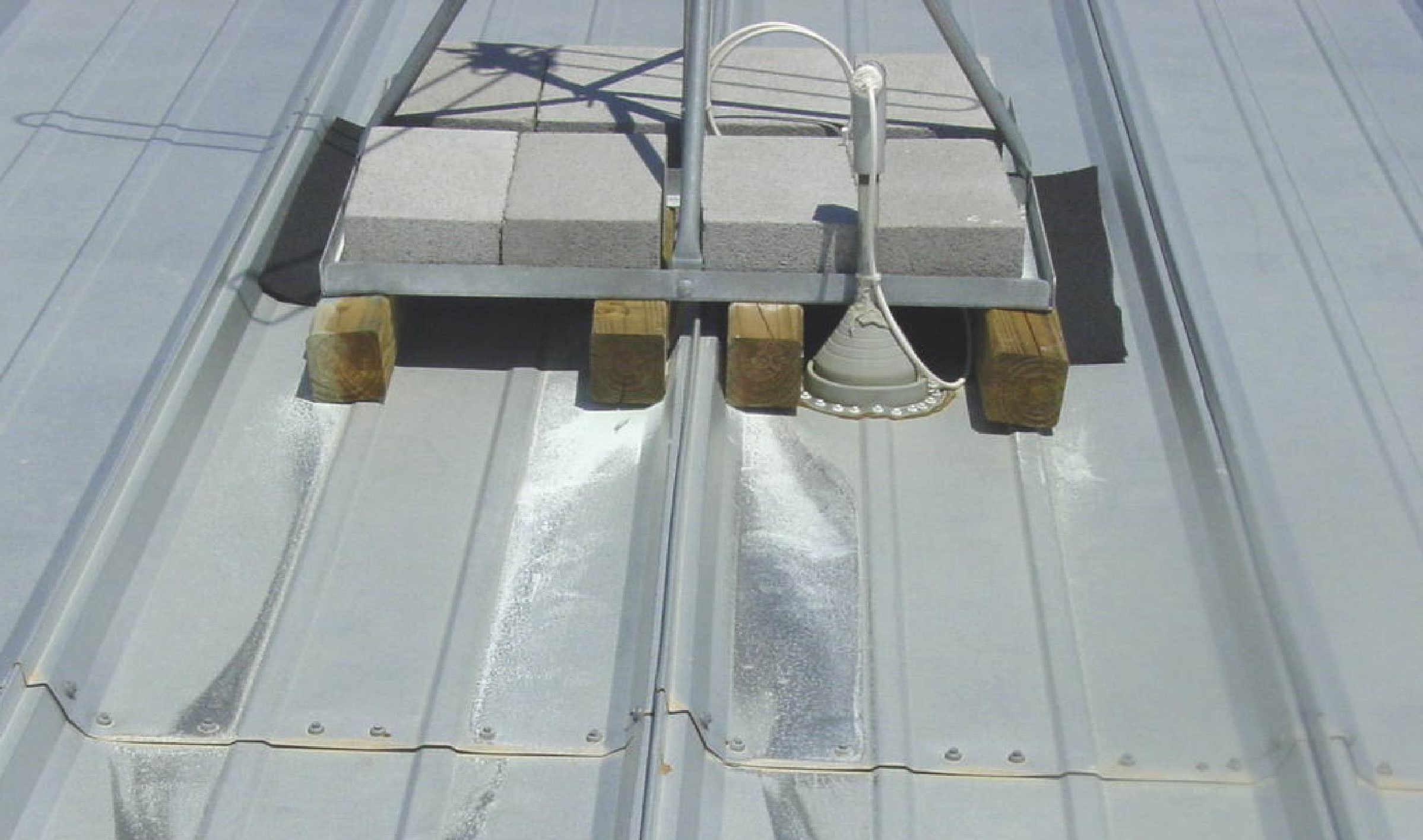

What To Do In Case of Rust
Let’s face it. Sometimes, despite all your efforts…someone didn’t get the memo and rust happens. Now what do you do? How can you safely can attempt to repair it or remove it without causing more damage?
First off, here’s what NOT to do. Heavy solvents that are meant to remove paint or stains can/will adversely affect the metal. If you witness a rust stain on the roof, don’t go up there with paint remover, acetone or any other toxic solvents and start scrubbing on it because you most likely could make matters worse. You might remove the stain along with the finish entirely, leading to bigger problems. (If you’re an end user, check your finish warranty and manufacturer maintenance documentation supplied to you by your builder/installer for guidance on cleaning and repairs.)
The key is to identify if the rust is just a stain /discoloration or it’s more systemic. Is the catalyst (ex.: a shaving) causing the rust still present? If it’s just a surface stain and the coating hasn’t been damaged, it might just be a matter of getting some mild detergents or something else to remedy the situation. Some good options are Formula 409 or Simple Green and Soft Scrub without bleach or something similar. and it may require a trial and error process to determine which is most effective based on the condition you’re trying to remedy. Products such as Rid O’ Rust or similar whose key ingredient is oxalic acid can be used diluted with water. With any of these products, test a small area first and wait to see results before proceeding to larger areas. And always be certain to fully rinse/flush areas of cleaning products to ensure no residues /films remain.
Always start light. Don’t break out any steel wool and/or metal grinders and start trying to get the rust off the panel that way. If it looks to be more than just a stain—perhaps you clean it and a few weeks later it comes back—that most likely means that the panel has actually been damaged and you’re not just going to get rid of the “stain” by cleaning it as it’ll return. It may require touchup paint or even a panel replacement. It depends on the severity of the damage. If this is the case, be certain to check with your installer, maintenance manual, and panel supplier for further instructions on how to address.
For more information on panel maintenance and warranties, see the MBCI website resource center.
Measuring for a Metal Roof: Considerations and Tips

Getting an accurate measurement for your metal roofing panels may seem like a no-brainer, but it’s not quite as simple as length x width. The many complexities of a roof must be taken into consideration in order to ensure your numbers add up. For instance, anything that intrudes upon a roof plane needs to be included in drawings with labeled measurements as these conditions will all affect the measurement but are sometimes overlooked.
Let’s look at some specific conditions to consider before getting out the measuring tape as well as some handy tips for installers.
Building Conditions to Consider Before Measuring
The type of roof system
Is it going to be a standing seam roof system or an exposed fastener system? Once you’ve decided on your roof type, we recommend reviewing all of the conditions/details on the roof. If it’s a standing seam roof, will the roof system need to float? If so, where will it be pinned, and what direction will it float?
At MBCI, we have published installation technical manuals for installers and erectors to utilize in order to familiarize themselves with how to adjust for ridge conditions or end lap conditions, for instance.
Is it a new or existing metal building?
If it is an existing building, are there new or updated building codes to consider? This could possibly dictate panel type, gauge, or width, or require additional framing members that could impact the final measurements.
What is the purlin spacing?
The panel break at the purlin for an endlap condition will need to be considered.
Are there extensions, overhangs or penetrations?
Include any roof extensions or overhangs that may not be apparent at first glance. Any and all roof conditions should be considered when calculating panel and trim length, including any roof penetrations such as pipes, roof curbs, skylight hatches, etc.
The manufacturer’s details will aid in determining such things as panel hold back at the ridge, or panel overhang at the eave or gutter. Also, roof or slope transitions, and panel hems should be considered.
Insulation
The thickness of the insulation could determine or dictate the fastener type used.
Measuring Tips
- Field verify the roof slope. The contractor should gather the field dimensions so measure when the framing is in place. While you can measure off of a set of plans, it’s not a definitive way to do things because things change in the field.
- The structure should be square while you’re measuring. Scaling from plans may get you close, but measuring erected framing that is plumb and square is the most accurate.
- You should measure multiple spots.
- It’s a good idea to use a plan view of the roof or sketch a bird’s eye view to record your measurements.
- Record your measurements in the units of measure that your manufacturer uses, typically feet and inches, to avoid errors.
- The erector may elect to add a few inches to the length of the panels at a hip or valley to remedy any cutting mishaps since these panels will be field cut to the hip or valley angle.
- Some contractors include one or two extra panels at the longest length for any errors or jobsite damage.
Ultimately, the takeaway is that any differential when measuring metal panels for installation could affect a building’s performance, so it’s important to keep all potential scenarios that could affect measurement accuracy in mind—throughout the entire process. To find out more about the proper way to measure a roof for metal buildings or to schedule training, contact your local MBCI representative.
Five Installer Responsibilities for Weathertightness Warranties
Every metal roof installation comes with an implied warranty: the roof shouldn’t leak. This is true even if your customer didn’t buy a “manufacturer’s weathertightness warranty.” It’s just the very basic expectation. Any details we send out, any materials, whatever the manufacturer supplies the installer…all go to that simple premise that you are buying a quality roof system from the get go.
Beyond that, though, a purchased manufacturer’s weathertightness warranty takes it a step further. It’s added insurance. In order to get the full value and peace of mind from a warranty, there are certain considerations the installer needs to keep in mind. Let’s take a look at five key installer responsibilities on projects with manufacturer weathertightness warranties—beyond, of course, putting down the roof correctly!
1. Understanding the weathertightness warranty type selected for the project.
MBCI sells two types of weathertightness warranties: Standard and Single Source. The approval process up front is the same for both but it is crucial to know the scope of the project’s warranty. With a standard warranty, the only real expectation is that the roof will remain watertight for 20 years. It is a very basic, very inexpensive warranty in which the manufacturer and the installer jointly warranty the roof for that period of time. The manufacturer covers all the materials and the details, and the installer is covering the installation.
The opposite end of that spectrum is the single source warranty, which is purchased when the customer wants not only the roof warrantied, but prefers everything associated with the roof—any accessories, anything else penetrating the roof—to be 100 percent covered by the manufacturer, if applicable. These warranties do cost more, require inspections, and require an installer to have completed the manufacturer’s certified installer training program.
It’s important for the installer to know what warranty was sold, particularly because he/she may not have been the one involved from the start. They may be coming in to bid the job as the installer only. Therefore, he/she needs to ask questions because they may or may not have the personnel on their crew that meets the requirements to install that roof for the weathertightness warranty purchased.
2. Obtaining/confirming building geometry approval for warranty.
Beyond the type of warranty, it is simultaneously necessary to investigate whether there are additional procedures related to the building geometry. Has everything been correctly noted so that the warranty itself will be valid? Is the manufacturer aware of transitions, edge conditions, roof penetrations, roof accessories (snow guards, solar, etc.)? It is extremely important to make sure that the geometry—or the conditions of the roof—are covered within a particular warranty.
MBCI, for instance, will review your roof plan and see the eave gutters, the ridge, the rake, etc. and we can survey what’s going on. Is that roof tying into something else? Will there be materials on that roof that aren’t provided by us or not being installed by the roof installer? As the manufacturer, we would be taking a cursory view to say, yes, we can warranty the roof or no, revisions are needed. If there is anything that we can’t warranty, we’re going to spell that out upfront. We will give as much direction as possible to get the project to a point it can be warranted.
That said, it’s the installer’s and customer’s responsibility to make sure that the manufacturer knows what’s happening. Think about it this way. Many times, there are other trades involved outside of the roofing contract. Along comes someone who says, “I need to run something through your roof,” or six months down the road the owner wants a satellite dish on the roof and the installer incorrectly penetrates the roof., causing a leak. Guess who they’re going to call? The installer/customer/owner needs to get that approved by the manufacturer. Otherwise, the warranty could be voided.
The main takeaways here: Do not make modifications to that roof without the manufacturer’s approval because the roof installer can end up inheriting the liability for that if they do. And, communicate the criteria or the requirements of the warranty to the customer. Don’t just hand them the paperwork. Make sure they understand what’s in it and their responsibilities as metal roof owners.
3. Ensure proper installer certification and training as required by the warranty type.
This sounds self-explanatory, but it goes back to the warranty type and the necessity to make sure the warranty selected is appropriate for the job. Verify whether or not the job requires a certified installer and if so, ensure certifications are current. If the installer is not certified, then they need to take the steps to get certified in order to meet that warranty requirement.
A common situation: A warranty gets sold by a general contractor and he/she subs it out to another roofing contractor. That sub comes in and says not to worry, “we know how to put the roof on. We’re certified.” Then, MBCI gets ready to issue the warranties or schedule inspections and finds out the subcontractor doesn’t know our system that well. And remember—for certain types of weathertightness warranties the installer needs to be certified via our training program.
4. The installer is responsible for correct installation per manufacturer’s details.
The onus is on the installer to follow the details and directions provided by the manufacturer. If you install the roof per those details, and then there’s a problem, the responsibility falls back on the manufacturer unless determined otherwise. If, however, the installer doesn’t follow the details provided and the manufacturer comes out to do a warranty claim or warranty inspection, then the installer is going to be responsible for correcting it. The installer can’t put it in wrong and just say, “oh, well, that’s covered by the warranty.” It’s not. A manufacturer’s warranty is not for covering a bad installation—particularly in the case of a standard warranty. If the installer does a poor install and the roof leaks, that’s not covered by the standard warranty; it falls back on the installer. Of note, this scenario can be different with a single source warranty, since the manufacturer will be out there doing ongoing inspections and ultimately can become responsible for the installation as well.
And, it goes without saying, the warranty doesn’t cover the interior contents of a building that may be damaged due to an installation issue.
5. Do not make adds or changes to an installed system once completed and the warranty has been issued without first getting manufacturer approval.
The warranty only covers the installed product per details, as mentioned. It does not cover additional materials added to the roof or any changes made, at least without the manufacturer’s prior approval—after the install is complete.
Some examples would be adding a mechanical unit to the roof, a plumbing vent added through the roof, or the satellite TV cable through the roof. Putting a penetration, fasteners, holes of any kind, into a previously installed roof system, unless approved by the manufacturer, will void the warranty in that location. If the manufacturer does not give approval, the installer, along with the customer, would need to make the decision—is it worth the risk to proceed knowing that if the roof leaks, that location would no longer by covered by the warranty.
To find out more about MBCI warranties and installer certification, contact your local MBCI representative or visit our website.
Maintaining Panel Modularity and Square When Installing a Metal Roof
Most metal roofing system installers know the importance of keeping panels on module, i.e., holding the width of the panel. But holding module alone isn’t enough; keeping panels square is equally important as the two go hand in hand. When proper attention is paid to both, you will have a faster install—ensuring longevity and functionality of the roof system so that it will be able to properly expand and contract as designed—not to mention improved appearance.
The ability to hold panel modularity is directly dependent upon several factors, including:
- Skillset of the installer
- Frequency that modularity is checked
- Substrate deficiencies
- Insulation system
- Appropriate methods being used to hold panel modularity during panel installation
- Keeping symmetry/maintaining squareness
Here are some important considerations for ensuring success for panel alignment.
The Relationship Between Holding Module and Squareness
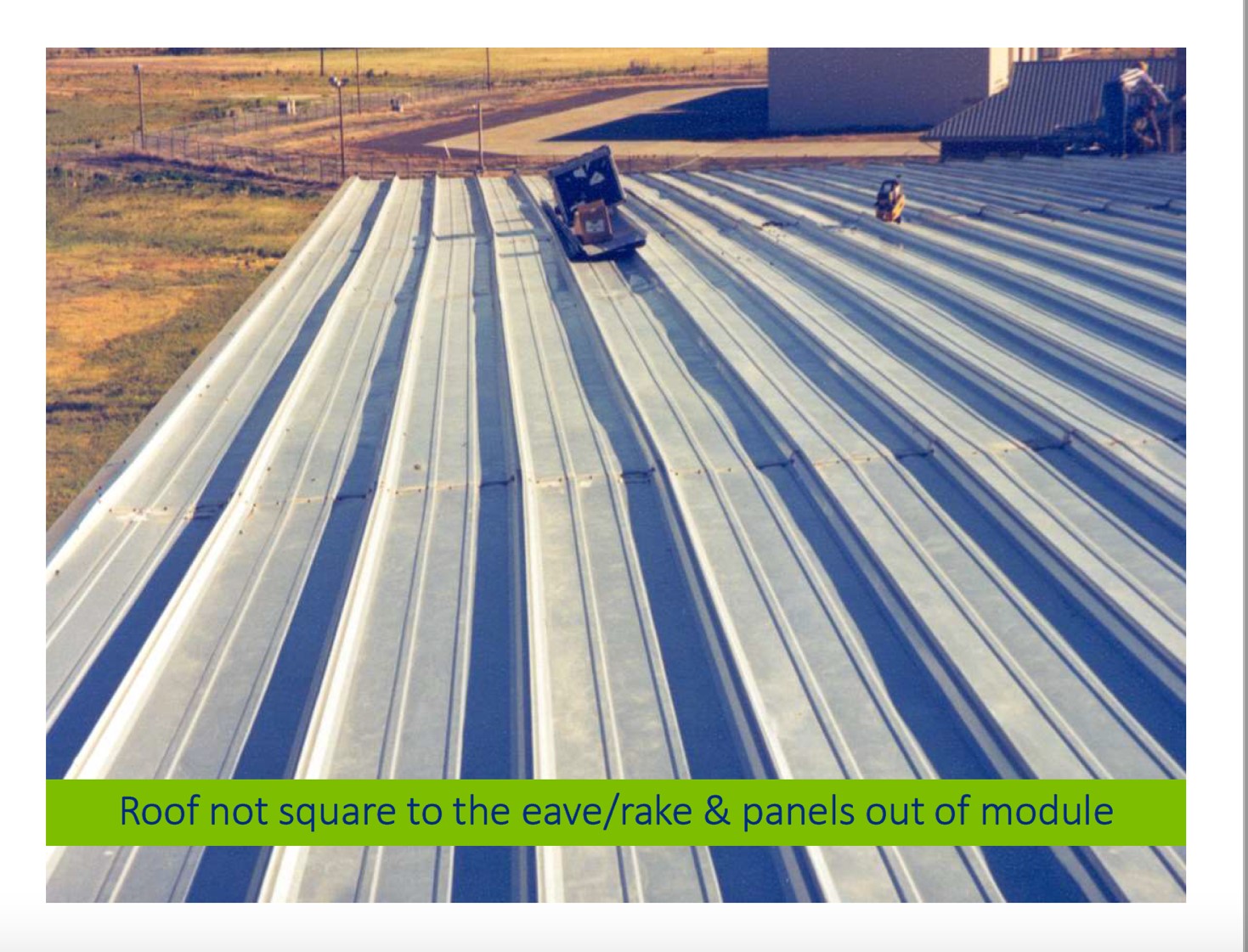
The roof panel is not going to “hold itself” 100% on module and square by installing just as received using only the hardware components supplied from the manufacturer. It is the installer’s responsibility to ensure the proper alignment and squareness of the panel install in order to hold panel module. For example, if you’re working with a 16-inch panel, installers need to keep the spacing of the panel ribs at 16 inches. In this way, the panel doesn’t become stretched or compressed. So, holding module is key along with holding square; the two are connected. If an installer doesn’t start the building out square, it will make it even harder to keep module with regards to the alignment of the panel.
As far as the overall appearance and performance, the success of the metal roof is going to be heavily dependent on how square it is installed and an ability to maintain proper modularity. There are a number of suggested methods for doing so outlined below. Installers must decide which method works best for their them and their roof panel application.
Methods to Ensure Success
The key method is measuring ahead and monitoring your installation so you know where you should be along that roof install. The metal panel is typically 24-gauge or 26-gauge material and therefore it’s easy enough to pull it ahead or have it become crowded during installation if you’re not staying close to your marks, and therefore it’s easy to get the panel out of module. The bigger impact, aside from just aesthetics of being on or off module is the performance of the system itself, to where it could become under stress or it could go through extra deformation due to being out of module and out of square. Its important to verify/measure the panels leading edge and adjust as needed via roof clips or other panel hardware. Some suggested methods include:
- Run a string line from eave to ridge square to the eave and measure from the string back to each panel run. The string line is moved ahead as the roof installation progresses. If installing over solid substrate, snap chalk lines for alignment points along the roof.
- Use a metal measuring tape permanently secured to the substrate at panel endlap locations, ridge and other intermediate points for permanent reference to check module.
- Mark the eave line for every rib installation to ensure the panel stays on module. Trapezoid panels offer metal closures for proper placement at the eaves to assist in holding module while vertical rib panels do not.
- Pre-drill substrates at the endlaps and ridge locations for clip alignment ahead of roof panel installation. A hole can be located at the leading edge of clip location so that an awl or punch can be inserted into the hold to align the clip and adjust accordingly. The holes drilled ahead of the panel at the corresponding panel module.
To assist with holding the panels’ shape when checking modularity, utilize outside panel closures or cut wood blocking to the panel’s correct width and insert between panel ribs. Note that a bad roof substrate that is out of tolerance for “flatness” will not be hidden or magically corrected by the panel installation. The alignment and tolerance of the substructure are equally critical to the panels’ squareness and being able to hold module. Substrate should be should be installed to a level plane tolerance that is no more than ¼” in 20-ft or 3/8” in 40-ft variance.
Do not stand in panel and/or keep as much weight as possible out of panel while installing clips. Not only is it unsafe but it changes the width of the panel and thus impacts modularity.
Use the correct combination of roof clip heights, insulation thickness and thermal spacers to maintain level panel installation and prevent panels from gaining or losing module. MBCI provides recommendations in its installation manuals regarding most common types of insulation thickness and means of attachment to various substrates. Additionally of note:
- Trimming of insulation or adjusting thermal block thickness can help control/modify panel modularity as needed.
- Alignment straps for trapezoid panels can be purchased from the manufacturer and installed on top of purlins before insulation. These set the clip spacing at 2-0” o.c and can be utilized at the endlap and ridge locations minimum or added at other locations.
At MBCI, we recommend that installers check module/square every three to four panels. If the panel grows or shrinks 1/8th of an inch or 3/16th of an inch with three or four panels or shows signs of being out of square, there’s time to recover from it by making adjustments to correct. If an installer just blindly puts the roof on for 50 feet or so and then realize they’re off module or out of square, it will likely be past the point of return to hold module and keep square.
For more information on installing metal roof panels to hold module, see our previous blog post on the topic.
For more information on our installer training sessions, click here, or submit your technical or installation questions by filling out our Ask An Expert form here.



