The beauty of metal roof system skylights can be a real benefit to the aesthetic value of a metal building project. Beyond looks, though, the proven benefits of daylighting are many: building occupant satisfaction from natural lighting, mold, mildew growth prevention, and, of course, energy savings, to name a few. In fact, once the decision has been made to go with metal for the roofing material, a skylight is often a natural tie-in when it comes to sustainable design—for both form and function. To make the most of the design choice, there are a few key considerations to bear in mind during the specification and pre-installation phases of the process.
Types of Metal Roof System Skylights
Common metal roofing skylight installation involves one of two types of skylights, Light Transmitting Panels (LTPs) and Curb Mount Skylights. Both metal roof system skylights supply natural light into the building and provide similar benefits.
LTPs, which are formed from a translucent material and come in many different panel profiles can be used not only in metal roofs but as an accessory for metal wall panels, too. One of the key benefits of LTPs is that the panel is formed so that it matches the configuration and characteristics of the system into which it is installed, and therefore can work seamlessly with specific metal roof systems.
Curbed (curb mount) skylights include a raised structure (“curb”) formed around the roof opening where the skylight will be attached. Curb skylights come in many shapes and styles.
In addition to the general “type” of the skylight, another consideration is selecting the best orientation for the skylight—which we will look at next.
Skylight installation Metal Roof Placement, Orientation, and Climate Factor
Placement and orientation are some of the most crucial factors in getting the maximum benefit from metal roof system skylights. During the planning phase, determine the best location to achieve optimal light and avoid obstructions (such as HVAC, plumbing, electrical, and vent pipes) below the skylight. In terms of getting the most out of the skylight from an energy-savings standpoint, climate, and exposure are also key factors. For example, with southern exposure, skylights provide an excellent level of passive solar heat during the colder winter months, while keeping cooling costs down during the summer heat. On the other hand, a skylight with western exposure will increase cooling costs if the structure is in a warm climate.
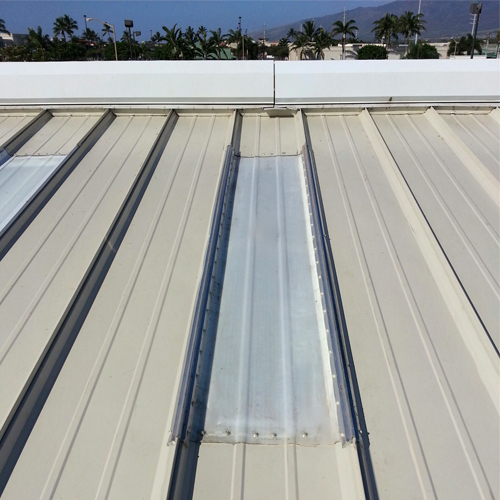

Installation Planning and Timing
Metal roof skylight installation can be installed during or after the roof has been installed, but it is in the best interest of the project to plan for a skylight from the initial stages of the design phase to best accommodate and prepare for the addition of the skylight.
Safety Concerns, Responsibility, and Compliance
Skylights and LTPs should be guarded to protect from fall through the metal railing, nets or some other protection method. Last but certainly not least, it must be stated that it is the user’s responsibility to ensure that the installation and use of all light transmitting panels comply with State, Federal and OSHA regulations and laws, including, but not limited to, guarding all light transmitting panels with screens, fixed standard railings, or other acceptable safety controls that prevent fall-through.
For additional information about skylights for metal roofs, please contact MBCI at (877) 713-6224.