A roof’s primary function is to keep a building weatherproof. A roof’s secondary function—and approaching nearly equal importance—is to be an energy-efficient element of the building envelope. From an energy efficiency standpoint, we’re accustomed to the inclusion of insulation. Are we as accustomed to the ideas that roof color and air leakage matter for energy efficiency? The building industry is embracing all of these technologies in an effort to save energy. So how does an installer make it all work?
Insulation
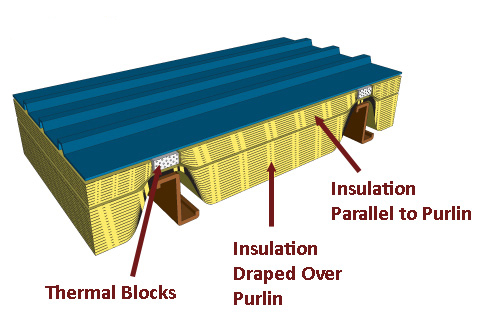
Insulation requirements for roofs on metal buildings (according to the 2015 IECC) range from R-19+R-11 LS up to R-30+R-11 LS, depending on climate zone. The first layer is draped over the purlins and requires a thermal spacer block with an R-3.5. A second layer is installed at perpendicular and is required to include a liner system (LS), which is a continuous vapor barrier installed below the purlins and is uninterrupted by framing members. The crisscrossed layers help reduce convective air movement within the insulation layer, making the insulation layer more effective. And, good news!—the vapor barrier can also be an air barrier. So, on to air barriers.
Air Barriers
Even small air leaks in buildings can account for a 30 to 40% heat loss during heating season (winter), regardless of the amount of insulation. It can’t be overstated—air barriers are critical to an energy-efficient roof and overall building envelope. The LS, or vapor barrier, can be an air barrier only if the seams of the LS are sealed to prevent air passage. The junction between the air barrier in the roof and walls is critical; it must be joined to be continuous. Often, a separate material (adhered membranes or spray-applied foams) is used as the transition from wall to roof. Or, the roof and wall air barriers might end on opposite sides of a perimeter beam or purlin, connecting the two air barriers. Also, any penetrations through the roof need to be sealed to the air barrier. Being continuous/having continuity is key to constructing a properly functioning air barrier!
Roof Color
We’ve heard a lot about roof color. Where air conditioning is prevalent (e.g., the Southwest), highly reflective roofs make sense, especially if there is minimal insulation. Where heating is prevalent, roof color becomes less effective for energy efficiency for a couple reasons. One, buildings require significant amounts of insulation, and two, there is much less direct heat gain from the sun over the course of a year. Where heating and cooling are both used regularly (e.g., Nashville, Chicago), it’s not a matter of “black or white.” There are many metal roof colors that are moderately reflective, so they balance reflectivity and heat gain as the seasons change.
Contemplate the interaction of insulation, roof color and air barriers on each metal roofing project.